|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Disease Conditions
- Abscess
- Acne
- Addiction
- Adenoid Hypertrophy
- Allergic Rhinitis or Hay Fever
- Alopecia Areata
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Amoebiasis
- Anxiety
- Asthma
- Backache
- Bed-Wetting-Enuresis
- Brain-Tumour
- Cataract
- Cirrhosis of Liver
- Conjunctivitis
- Constipation
- Dengue
- Depression
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Diseases of Prostate
- Eczema
- Epilepsy
- Erectile-Dysfunction
- Gallstones
- Goitre
- Gynaec
- Hepatitis
- Hepatitis-a
- Hepatitis-b
- Hepatitis-e
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- IBS - Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Infertility
- Infertility FAQ
- Male Infertility
- Male Infertility FAQ
- Women Infertility
- Lichen Planus
- Lipoma
- Meningitis
- Menstrual-Disorders
- Migraine
- Molluscum-Contagiosum
- Nasal-Polyps
- Neoplasm
- Nephrotic Syndrome
- Neuralgia
- Osteo Arthritis
- Otitis
- Piles or Hemorrhoids
- Premature-Ejaculation
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Ringworm
- Schizophrenia
- Sinusitis
- Spondylitis
- Styes
- Tarsal Cyst-Chalazion
- Tonsilitis
- Typhoid
- Urinary-Tract-Infection
- Urticaria
- Vertigo
- Vitiligo
- Warts
Auroh Health Horoscope
Disease A - Z > Gallstones > Homeopathic treatment for Gallstones
Homeopathy treatment for Gallstones
|
||||||||
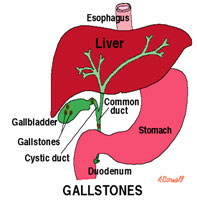
Gallstones are small, pebble-like substances that develop in the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped sac located below your liver in the right upper abdomen. Gallstones form when liquid stored in the gallbladder hardens into pieces of stone-like material. The liquid—called bile—helps the body digest fats. Bile is made in the liver, then stored in the gallbladder until the body needs it. The gallbladder contracts and pushes the bile into a tube—called the common bile duct—that carries it to the small intestine, where it helps with digestion
 |
 |
Bile contains water, cholesterol, fats, bile salts, proteins, and bilirubin—a waste product. Bile salts break up fat, and bilirubin gives bile and stool a yellowish-brown color. If the liquid bile contains too much cholesterol, bile salts, or bilirubin, it can harden into gallstones
Types of gall stones
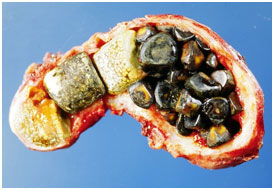
The two types of gallstones are cholesterol stones and pigment stones. Cholesterol stones are usually yellow-green and are made primarily of hardened cholesterol. They account for about 80 percent of gallstones. Pigment stones are small, dark stones made of bilirubin. Gallstones can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. The gallbladder can develop just one large stone, hundreds of tiny stones, or a combination of the two
Gallstones can block the normal flow of bile if they move from the gallbladder and lodge in any of the ducts that carry bile from the liver to the small intestine. The ducts include the
- hepatic ducts, which carry bile out of the liver
- cystic duct, which takes bile to and from the gallbladder
- common bile duct, which takes bile from the cystic and hepatic ducts to the small intestine
Bile trapped in these ducts can cause inflammation in the gallbladder, the ducts, or in rare cases, the liver. Other ducts open into the common bile duct, including the pancreatic duct, which carries digestive enzymes out of the pancreas. Sometimes gallstones passing through the common bile duct provoke inflammation in the pancreas—called gallstone pancreatitis—an extremely painful and potentially dangerous condition
If any of the bile ducts remain blocked for a significant period of time, severe damage or infection can occur in the gallbladder, liver, or pancreas. Left untreated, the condition can be fatal. Warning signs of a serious problem are fever, jaundice, and persistent pain
What causes gallstones ?
Scientists believe cholesterol stones form when bile contains too much cholesterol, too much bilirubin, or not enough bile salts, or when the gallbladder does not empty completely or often enough. The reason these imbalances occur is not known
The cause of pigment stones is not fully understood. The stones tend to develop in people who have liver cirrhosis, biliary tract infections, or hereditary blood disorders—such as sickle cell anemia—in which the liver makes too much bilirubin
The mere presence of gallstones may cause more gallstones to develop. Other factors that contribute to the formation of gallstones, particularly cholesterol stones, include
- Sex. Women are twice as likely as men to develop gallstones. Excess estrogen from pregnancy, hormone replacement therapy, and birth control pills appears to increase cholesterol levels in bile and decrease gallbladder movement, which can lead to gallstones
- Family history. Gallstones often run in families, pointing to a possible genetic link
- Weight. A large clinical study showed that being even moderately overweight increases the risk for developing gallstones. The most likely reason is that the amount of bile salts in bile is reduced, resulting in more cholesterol. Increased cholesterol reduces gallbladder emptying. Obesity is a major risk factor for gallstones, especially in women
- Diet. Diets high in fat and cholesterol and low in fiber increase the risk of gallstones due to increased cholesterol in the bile and reduced gallbladder emptying
- Rapid weight loss. As the body metabolizes fat during prolonged fasting and rapid weight loss—such as “crash diets”—the liver secretes extra cholesterol into bile, which can cause gallstones. In addition, the gallbladder does not empty properly
- Ethnicity. American Indians have a genetic predisposition to secrete high levels of cholesterol in bile. In fact, they have the highest rate of gallstones in the United States. The majority of American Indian men have gallstones by age 60. Among the Pima Indians of Arizona, 70 percent of women have gallstones by age 30. Mexican American men and women of all ages also have high rates of gallstones
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs. Drugs that lower cholesterol levels in the blood actually increase the amount of cholesterol secreted into bile. In turn, the risk of gallstones increases
- Diabetes. People with diabetes generally have high levels of fatty acids called triglycerides. These fatty acids may increase the risk of gallstones
Who is at risk for gallstones ?
People at risk for gallstones include
- women—especially women who are pregnant, use hormone replacement therapy, or take birth control pills
- people over age 60
- American Indians
- Mexican Americans
- overweight or obese men and women
- people who fast or lose a lot of weight quickly
- people with a family history of gallstones
- people with diabetes
- people who take cholesterol-lowering drugs
What are the symptoms of gallstones ?
As gallstones move into the bile ducts and create blockage, pressure increases in the gallbladder and one or more symptoms may occur. Symptoms of blocked bile ducts are often called a gallbladder “attack” because they occur suddenly. Gallbladder attacks often follow fatty meals, and they may occur during the night. A typical attack can cause
- steady pain in the right upper abdomen that increases rapidly and lasts from 30 minutes to several hours
- pain in the back between the shoulder blades
- pain under the right shoulder
Notify your doctor if you think you have experienced a gallbladder attack. Although these attacks often pass as gallstones move, your gallbladder can become infected and rupture if a blockage remains.
People with any of the following symptoms should see a doctor immediately
- prolonged pain—more than 5 hours
- nausea and vomiting
- fever—even low-grade—or chills
- yellowish color of the skin or whites of the eyes
- clay-colored stools
Many people with gallstones have no symptoms; these gallstones are called “silent stones.” They do not interfere with gallbladder, liver, or pancreas function and do not need treatment
How are gallstones diagnosed ?
Frequently, gallstones are discovered during tests for other health conditions. When gallstones are suspected to be the cause of symptoms, the doctor is likely to do an ultrasound exam—the most sensitive and specific test for gallstones. A handheld device, which a technician glides over the abdomen, sends sound waves toward the gallbladder. The sound waves bounce off the gallbladder, liver, and other organs, and their echoes make electrical impulses that create a picture of the gallbladder on a video monitor. If gallstones are present, the sound waves will bounce off them, too, showing their location. Other tests may also be performed
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan. The CT scan is a noninvasive x ray that produces cross-section images of the body. The test may show the gallstones or complications, such as infection and rupture of the gallbladder or bile ducts
- Cholescintigraphy (HIDA scan). The patient is injected with a small amount of nonharmful radioactive material that is absorbed by the gallbladder, which is then stimulated to contract. The test is used to diagnose abnormal contraction of the gallbladder or obstruction of the bile ducts
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). ERCP is used to locate and remove stones in the bile ducts. After lightly sedating you, the doctor inserts an endoscope—a long, flexible, lighted tube with a camera—down the throat and through the stomach and into the small intestine. The endoscope is connected to a computer and video monitor. The doctor guides the endoscope and injects a special dye that helps the bile ducts appear better on the monitor. The endoscope helps the doctor locate the affected bile duct and the gallstone. The stone is captured in a tiny basket and removed with the endoscope
- Blood tests. Blood tests may be performed to look for signs of infection, obstruction, pancreatitis, or jaundice
AUROH Homeopathy Treatment
AUROH homeopathy has proved in treating gall stones .Since many years of research with the excellent team of doctors helped many patients all over the world to get treated wonderfully. AUROH homeopathy has good effective medicines in dissolving these gallstones without any necessity of surgery at the initial stages of disease progress. Mostly the small sized gall stones can be easily dissolved at the initial stages of the disease. The general symptoms accompanied in gall stones or any other disease form along with gall stones can be treated with homeopathic medicines
AUROH homeopathic medicines act so well that the tendency of forming stones can be stopped .To stop this tendency of stone formations, these medicines play a major role genetically with no side effects
Exceptionally at times few cases having large and multiple stones needs immediate surgery. In such cases AUROH recommends for immediate surgery and can start homeopathic medicines after surgery to avoid recurrence of stone formations
homeopathy is 200 years old and was discovered by a German Orthodox Physician, Samuel Christian Hahnemann. It is an effective and statistically proven systems of healing which assists the natural tendency of the body to heal itself, it recognises that all symptoms of ill health are expressions of disharmony within the whole person and that it is the patient who needs treatment not the disease
The challenge facing the Homeopath is to find the “medicine of the moment” for the person at the time Homeopathic remedies work by stimulating the body’s own healing power. This power is very great and many complaints heal themselves unaided, but when the healing process is faulty, blocked or slow the Homeopathic remedy acts as a stimulus to the curative powers of the body
In order to find the right remedy, the Homeopath will interview the patient extensively about their medical history, family history and general state of mind in addition to delving into the symptoms of the illness that prompted their visit
Homeopathic remedies are non-addictive and have no side effects. Sometimes there can be a temporary aggravation of the condition which, needs to be treated - this is normal and demonstrates that the treatment is working
| talk to our doctors right now |  |
|
| consult our experts | ||
 |
leave your number we will call you back |
|
| start auroh health treatment |
Your doctor is just a click away |
Treatment |